Human head
About the human head
The human head is the upper part of the human body and contains the brain, which is the body's control center. It is also the site of the sense organs, such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth, as well as the site of important structures such as the jaw and teeth, and the face and neck muscles that are used for communication and expression. The head also houses the spinal cord, which is protected by the skull, a bony structure that encases and protects the brain.
The human head is made up of several bones, including the skull, which is composed of the cranium and the face. The cranium is a protective shell that covers the brain, while the face contains openings for the eyes, nose, mouth, and other structures. The head is also home to a complex network of blood vessels, nerves, and muscles that help to control the body's functions and support movement and sensation.
In addition to its physical structure, the human head is also important in terms of culture, identity, and self-expression. The face and head are used to communicate and convey emotions, and they are often the first thing that people notice about each other. As such, the human head is a source of great fascination and has been the subject of study in fields such as anatomy, neuroscience, and psychology.
The brain is the central organ of the nervous system and is considered the control center of the body. It is responsible for coordinating and controlling various functions, including movement, sensation, thought, emotion, and the regulation of various bodily systems. The brain is also the site of consciousness, where perceptions, thoughts, and memories are processed and stored.
About human brain
The human brain is divided into several distinct regions, each of which is responsible for specific functions. These regions include the cerebral cortex, the brainstem, and the cerebellum, among others. The cerebral cortex is the outer layer of the brain and is responsible for the majority of higher brain functions, such as perception, memory, thought, and voluntary movement. The brainstem is located at the base of the brain and is responsible for controlling essential functions such as breathing and heart rate. The cerebellum is located at the base of the brain and is responsible for coordinating movement and maintaining balance.
The brain is made up of billions of nerve cells, or neurons, and supportive cells known as glia. These cells communicate with each other through a complex network of electrical and chemical signals, which allow the brain to process information, coordinate movement, and control various bodily functions. The brain is also constantly changing and adapting in response to experiences, a process known as neuroplasticity.
Overall, the brain is an incredibly complex and sophisticated organ that plays a critical role in determining who we are and how we experience the world. Understanding the brain and how it works is a major focus of research in fields such as neuroscience, psychology, and medicine.
The human eye is an amazing organ that allows us to see and perceive the world around us. It is a complex structure that consists of several parts, including the cornea, lens, iris, retina, and optic nerve. These parts work together to capture light, focus it onto the retina, and transmit visual information to the brain, where it is processed and interpreted.
The cornea is the clear outer layer of the eye that helps to protect it and focuses incoming light. The lens, located behind the cornea, helps to further focus light onto the retina. The iris is the colored part of the eye that surrounds the pupil and controls the amount of light that enters the eye. The retina is the innermost layer of the eye that contains specialized cells known as photoreceptors, which capture light and convert it into electrical signals that are sent to the brain. The optic nerve carries these electrical signals from the retina to the brain, where they are interpreted as images.
About the human eyes
The human eye is capable of detecting a wide range of light levels, from bright sunshine to the dimmest of starlight, and it can quickly adjust to different lighting conditions. It is also capable of perceiving a wide range of colors and can distinguish fine details and textures. The eyes also play a critical role in maintaining balance and coordinating movement.
Overall, the human eye is a remarkable organ that allows us to experience the world in a rich and vivid way. However, like all organs, the eye is subject to a variety of conditions and diseases that can impair vision. Some common eye conditions include nearsightedness, farsightedness, cataracts, glaucoma, and age-related macular degeneration. Regular eye exams and early detection and treatment of eye conditions are important for maintaining good vision and overall eye health.
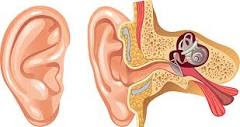
About the human ears
The human ear is a complex sensory organ that plays a critical role in hearing and maintaining balance. The ear is divided into three main parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Each part has a unique structure and function that contributes to the overall ability to hear and maintain balance.
The outer ear is made up of the visible portion of the ear, called the pinna or auricle, and the ear canal. The pinna collects and directs sound waves into the ear canal, which leads to the eardrum.
The middle ear contains the eardrum, a thin membrane that vibrates in response to sound waves, and three small bones called the ossicles (the malleus, incus, and stapes), which transmit the vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear.
The inner ear is a complex structure that contains the cochlea, a spiral-shaped organ that is responsible for converting the vibrations from the middle ear into electrical signals that are sent to the brain. The inner ear also contains the vestibular system, which is responsible for maintaining balance and detecting changes in head position.
The ear plays a critical role in our ability to hear and understand sounds, as well as in our ability to maintain balance and coordination. Some common ear conditions that can impair hearing and balance include otitis media (middle ear infection), tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and presbycusis (age-related hearing loss). Regular hearing exams and prompt treatment of ear conditions can help to maintain good hearing and balance.
The human nose
The human nose is a complex organ that plays a critical role in the sense of smell, as well as in breathing and maintaining proper air moisture and temperature.
The nose is made up of several parts, including the nostrils, the nasal cavity, and the olfactory epithelium. The nostrils are the openings in the nose that allow air to enter. The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space behind the nostrils that warms, moistens, and filters the air that we breathe. The olfactory epithelium is a specialized area in the nasal cavity that contains the receptor cells for the sense of smell.
The sense of smell is a critical component of our ability to experience and enjoy the world around us. Odors from the environment are detected by the olfactory receptor cells, which send signals to the brain that are interpreted as specific scents. The sense of smell is also closely linked to our ability to taste, as the sense of taste and smell are closely intertwined in the brain.
In addition to the sense of smell, the nose also plays a critical role in maintaining proper air moisture and temperature and filtering out foreign particles, such as dust and bacteria, that we breathe in. The nasal passages are lined with tiny hairs and mucus-secreting glands, which help to trap foreign particles and prevent them from entering the lungs.
Overall, the human nose is a complex and important organ that plays a critical role in our ability to experience and enjoy the world around us, as well as in our overall health and well-being. Some common conditions that can affect the nose include the common cold, sinusitis, and nasal allergies. Regular preventive care and prompt treatment of these and other conditions can help to maintain good nasal health.
The human mouth
The human mouth is a complex and multifunctional organ that plays a critical role in several important bodily processes, including eating, speaking, breathing, and maintaining good oral health.
The mouth is made up of several parts, including the lips, the teeth, the tongue, the gums, the salivary glands, and the pharynx. The lips serve as the opening to the mouth and help to form and shape words during speech. The teeth, which are embedded in the gums, are used for chewing and grinding food. The tongue is a muscular organ that helps to mix and manipulate food in the mouth, as well as plays a critical role in speech. The gums, which surround the teeth, help to protect the roots of the teeth and anchor them in place. The salivary glands produce saliva, which moistens the mouth and helps to begin the process of breaking down food. The pharynx is part of the mouth that leads to the throat and serves as a common passage for both food and air.
Eating is one of the most important functions of the mouth, as it provides the body with the necessary nutrients and energy to function properly. The mouth also plays a critical role in speech, as it helps to form and shape words, and in breathing, as it allows air to enter and exit the body.
Maintaining good oral health is also important, as the mouth is home to a complex community of bacteria that can cause oral health problems if not properly cared for. Regular brushing and flossing, as well as regular dental check-ups, can help to maintain good oral health and prevent problems such as tooth decay and gum disease.
Overall, the human mouth is a complex and important organ that plays a critical role in several important bodily processes. Regular preventive care and prompt treatment of oral health problems can help to maintain good oral health and prevent serious health problems.